The BHSA Transition Guide Part 4: Ensuring Effective Stakeholder Engagement and Community Planning Strategies
In our previous post, we introduced EVALCORP’s Behavioral Health Services Act (BHSA) Compliance & Integration Workgroup and the comprehensive resources we’ve developed to support behavioral health organizations through this transition. Since then, we’ve been working directly with counties to address the practical realities of implementing BHSA requirements while managing existing programs and stakeholder relationships.
As the fourth post in our BHSA transition series, we address four key questions that counties have asked our team while moving towards new state requirements for the community planning process:
- How can county governments frame the changes under the BHSA when engaging stakeholders during the community planning process?
- What strategies can county governments use to ensure meaningful engagement with diverse stakeholders, including traditionally underserved populations?
- During this transition, county governments, partners, and facilitators may need to engage in community conversations where emotions or differing viewpoints are high. How can county governments ensure groups stay focused on the goals while still making everyone feel heard and respected?
- What are some specific tools and/or strategies county governments can utilize to support the community planning process, such as needs assessment or strategy prioritization tools?
As always, EVALCORP remains committed to helping our county partners navigate this transition thoughtfully and strategically, ensuring alignment with state expectations while addressing local behavioral health needs. There are several key BHSA deadlines over the next four years, and we are here to support you at each step of the process.
1) Communicate The Complexity of the BHSA Change
Key Question: How can county governments frame the changes under the BHSA when engaging stakeholders during the community planning process?
This transformation requires a delicate balance of strategic vision, operational pragmatism, and community engagement. When framing this shift to stakeholders, counties should highlight both the opportunities and challenges of this transition, while presenting it as a chance for integrated care and a whole-person approach. We recommend using the messaging pillars below.
Four Key Messaging Pillars
1. Acknowledge the Significance & Vision
This is an opportunity to recognize the urgent need to address the intersection of behavioral health and homelessness. BHSA provides a critical framework and resources to tackle this challenge head-on, moving counties closer to a more integrated, person-centered system that holistically addresses mental health, substance use, and housing needs. It’s an opportunity to enhance the continuum of care and ensure services are more impactful and outcome-driven.
2. Express Operational Challenges & Concerns
While the vision is clear, the operationalization of Proposition 1 is incredibly complex. Counties are meticulously working through the intricacies of realigning funding streams and adapting existing programs. Primary concerns include managing the reallocation of funds, particularly the impact on Prevention and Early Intervention (PEI) and Full Service Partnership (FSP) programs, as well as workforce development needs and enhanced data reporting requirements.
EVALCORP is currently providing support to several counties in assessing their workforce needs and identifying areas where they’ll need to develop new expertise, particularly in housing navigation and integrated care models. There’s an understandable anxiety among both staff and clients about these changes, particularly concerning the potential impact on existing programs. We also provide support with the increased data reporting and accountability requirements, enhancing counties’ data infrastructure and analytical capabilities to effectively demonstrate their impact.
3. Emphasize Collaboration & Community
This transition cannot be accomplished in isolation. Counties must actively engage with all community partners, such as providers, housing agencies, law enforcement, clients, and community-based organizations, to ensure a collaborative and inclusive planning process. This is an opportunity to strengthen partnerships across sectors, particularly with housing, social services, and primary care, to build a truly integrated support system.
4. Adopt a Forward-Looking and Determined Stance
This transition presents both challenges and immense opportunities. Counties can leverage these new resources to build a more resilient, responsive, and recovery-oriented behavioral health system for their most vulnerable residents.
2) Develop Strategies for Meaningful Stakeholder Engagement
Key Question: What strategies can governments use to ensure meaningful engagement with diverse stakeholders, including traditionally underserved populations?
Effective stakeholder engagement under BHSA involves the following key principles:
- Cultural Humility & Competence: Approach all interactions with respect for diverse perspectives and experiences
- Trauma-Informed Approach: Recognize the impact of trauma on participants and create safe, supportive environments
- Equity-Driven: Prioritize voices of traditionally underserved populations
- Transparency & Feedback Loop: Maintain open communication about how input is being incorporated
- Accessibility: Ensure all participants can meaningfully contribute regardless of barriers
3) Manage Community Conversations
Key Question: During this transition, county governments, partners, and facilitators may need to engage in community conversations where emotions or differing viewpoints are high. How can governments ensure groups stay focused on the goals while still making everyone feel heard and respected?
At EVALCORP, when we facilitate community conversations, our focus is on making sessions productive and respecting individual experiences while generating practical insights for enhancing services. Our team follows these core principles to achieve productive community conversations:
Before Facilitation
Robust Preparation: Establish clear ground rules, implement trauma-informed approaches, develop emotional management plans, and utilize co-facilitation models.
Purpose & Confidentiality: Explicitly state session goals (understanding experiences, not debating) and ensure confidentiality protections are clear.
During Facilitation
Listen Actively: Hear and reflect participants’ contributions to ensure they feel genuinely heard and valued.
Gently Redirect: When emotions rise or discussions drift, calmly realign the conversation to core objectives without dismissing concerns.
Enable Equitable Participation: Actively manage speaking time and create multiple pathways for contribution to ensure all voices can participate.
Focus on “What” & “How”: Shift conversations from personal attacks or blame toward systemic issues, impacts, and potential solutions.
Acknowledge & Park: Recognize important but off-topic points for later follow-up while maintaining session focus.
Provide Breaks/Space: Offer moments to reset when tension is particularly high.
Through these approaches, counties can conduct productive sessions that honor individual experiences while generating actionable insights to improve services and inform BHSA planning.
4) Practical Tools and Strategies for Community Planning
Key Question: What are some specific tools and/or strategies governments can utilize throughout the community planning process, such as needs assessment or strategy prioritization tools?
The most effective community planning processes are those that are intentional, data-driven, and focused on actionable outcomes. Counties should avoid the common pitfall of gathering broad input without the capacity to act on feedback, which can lead to stakeholder frustration and disengagement.
Before engaging stakeholders, counties should complete a systematic 4-step behavioral health needs assessment that informs the entire Community Planning Process:
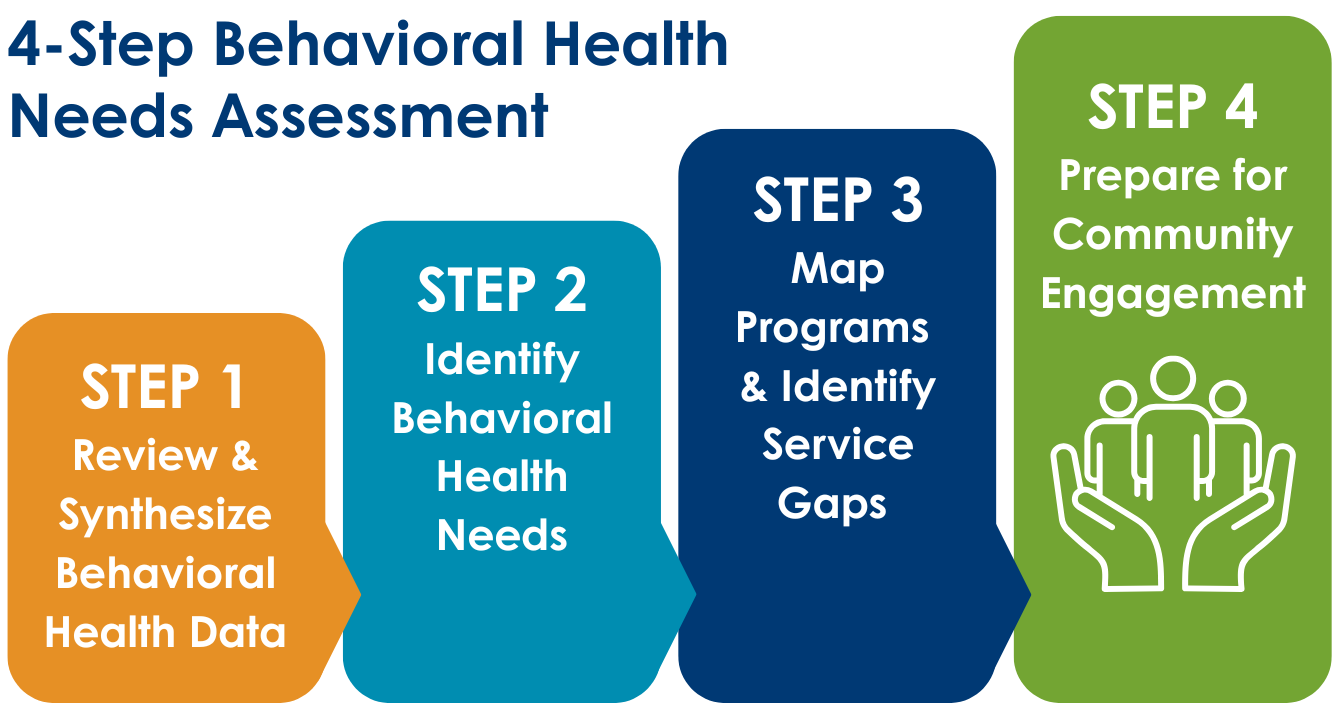
Step 1: Review and Synthesize Behavioral Health Data
Review and synthesize existing behavioral health data, organizing findings according to the Statewide Behavioral Health Goals. This foundational step ensures that community engagement is grounded in evidence and aligned with state requirements from the outset.
Step 2: Identify Behavioral Health Needs
Identify priority behavioral health needs by interpreting synthesized data for gaps, disparities, and trends across each goal. This analysis identifies the areas where the greatest needs exist, helping to focus stakeholder conversations on the most critical issues.
Step 3: Map Programs and Identify Service Gaps
Map existing programs and services to identified behavioral health needs, highlighting areas where gaps in service delivery persist. This step is crucial for understanding what resources are already available and where new or enhanced services may be needed.
Step 4: Prepare for Community Engagement
Design an engagement plan and tools informed by service gaps and ensure that community input sessions are strategic, focused, and designed to generate actionable insights.
Key Takeaways for Intentional Outreach
The principles below provide strategies to help ensure community planning processes are intentional and achieve their desired impact.
Ask About Things Counties Can Actually Act On: Focus community input specifically on areas where counties have realistic capacity to implement changes. This means being transparent about funding constraints, regulatory requirements, and organizational limitations while still seeking creative solutions within those parameters. When stakeholders understand the boundaries within which change is possible, their input becomes more strategic and actionable.
Ensure that the scope of feedback requested aligns with the county’s organizational capacity to respond and implement changes. This prevents the cycle of gathering extensive input that ultimately cannot be acted upon due to resource or regulatory constraints.
Organize Conversations Around Priority Populations: Focus discussions on the specific groups outlined in BHSA requirements, such as individuals experiencing homelessness, those with serious mental illness, and other key populations. This targeted approach keeps the most vulnerable community members at the center of planning. Additionally, structure conversations to emphasize outcomes and cover as many metrics as possible — whether population-based or state-level — to ensure compliance with DHCS guidelines and requirements.
Engage the Service Continuum: Gather input across all levels of care and intervention, from prevention and early intervention through crisis response to ongoing support services. This comprehensive approach helps identify gaps and opportunities for integration across the behavioral health system.
Be Transparent and Foster Close Collaboration Through Regular Check-Ins: Share findings frequently through recurring meetings with key stakeholders, rather than waiting for formal reporting periods. This ongoing dialogue helps maintain engagement and allows for course corrections throughout the planning process. Use continuous feedback to improve both the planning process itself and the resulting service delivery approaches.
Looking Forward: EVALCORP’s Continued Support
EVALCORP’s BHSA Compliance and Integration Workgroup continues to track developments and provide hands-on support to counties across California. From community engagement strategy development to facilitation support and outcome reporting, EVALCORP is ready to support you through every stage of this transition.